Majid Taromi, Maziar Hosseini, Seyed Mahdi Pourhashemi, Majid Sadeghi,
Volume 11, Issue 1 (Vol. 11, No. 1 Spring 2017 2017)
./files/site1/files/3Extended_Abstract.pdfExtended Abstract
(Paper pages 51-72)
Introduction
Value engineering is considered an efficient alternative to improve design and construction process of urban tunneling projects. Application of value engineering techniques can provide investigating all aspects of a project in a team work, creative and short-time manner which contribute to precisely identify a project’s quality improvement issues, construction time and costs.
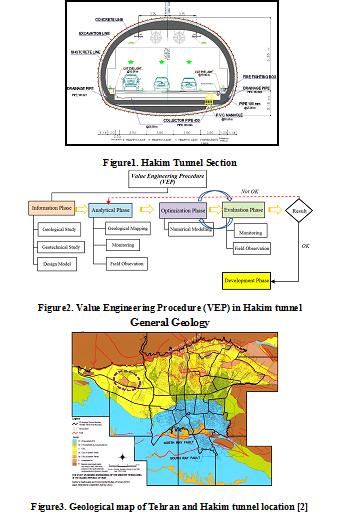
Hakim Expressway one of the capital's main highways in Tehran metropolis with 9 Km in length, starts from the junction of Resalat expressway and Kurdistan expressway after Resalat tunnel and ends in Lashgari expressway. The west extended this highway passing through the area of Chitgar forest park. Due to environmental constraints, the Hakim twin tunnels with cross-section of 186 m
2 excavation areas and total length of 3256 m to the NATM/SEM method in this area were excavated (Figure 1).
In preliminary design of Hakim tunnel project, on category of excavation and support system was suggested. During the tunnel
’s excavation operation, the behavior and classification of the tunnel were investigated from field observation, instrumentation and monitoring of geological models and subsequently, further excavation process was modified in accordance with value engineering. The aim of using value engineering approach in this project was to reduce the costs without any decrease in quality, employer satisfaction along with minimum risk and as well as improving operational and practical aspects. Ultimately, establishment of the value engineering approach on Hakim tunneling project leads to 10% reduction in construction costs as well as relevant quality with the least challenges (Figure 2).
General Geology
The city of Tehran is founded on Quaternary alluvium, which has been geologically classified by Rieben [1]. The city is located at the foot of the Alborz mountain range, which is basically composed of Eocene pyroclastic deposits (green tuff) and other volcanic rocks. The geology and the morphology of the Tehran region is similar to that for other cities located at the foot of mountains.
Rieben (1966) divided the Tehran coarse-grained alluvia into four categories, identified as A, B, C and D, where A is the oldest and D the youngest (Figure 3).
Hakim tunnel project locates on foothills of northern Tehran, crossing the hills of Chitgar forest park. Results of field surveys indicate that alluvial deposits in tunnel track belong to C (ramps and tunnel portal) and A formations (in most parts of tunnel track).
 Geotechnical characterization
Geotechnical characterization
Table1 summarizes soil input parameters. Two soil types were considered for the model with 8- meter-height overburden. First layer (No.1) starts from surface with a 1 meter thickness. Second layer (No. 2) has 7 meter thickness.
Table1. Summary of the geotechnical parameters
| Parameter |
Unit |
Layer No. 1 |
Layer No. 1 |
| Internal friction angle (CU) |
Deg. |
29 |
33 |
| Cohesion (CU) |
Kg/cm2 |
0.15 |
0.45 |
| Density |
Kg/cm3 |
18.5 |
20 |
| Poisson ratio of unloading/reloading |
Kg/cm2 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
| Secant deformation modulus |
Kg/cm2 |
550 |
900 |
| Power of stress level of stiffness |
|
0.5 |
0.5 |
| Stiffness unloading |
Kg/cm2 |
1650 |
2700 |
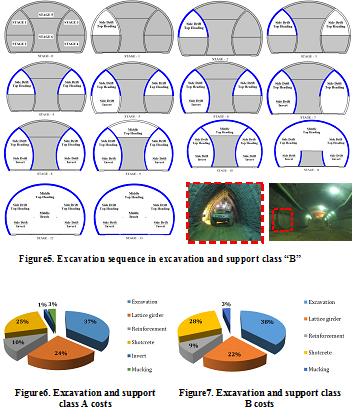
During tunnel excavation using field observations, the results of the monitoring and reviewing the geological model, ground behavior and classification were re-examined to optimization of the excavation and support class (Figures 4, 5).
Detailed analysis before excavation and continuation of studies led to two excavation and support classes purposed for Hakim tunnel. Both classes of excavation and support due to ground conditions are modeled and analyzed using software Plaxis. For verification, the results of numerical analysis using monitoring and field observations were compared during the tunnel excavation. The results of monitoring compliance with the results of numerical analysis were appropriate.
Implementation and construction costs were calculated for different sections of two excavation and support classes in accordance to contraction documents to evaluate the effect of optimization in design (Figures 6, 7)
.jpg) Figure4. Excavation sequence in excavation and support class “A”
Figure4. Excavation sequence in excavation and support class “A”
 Results
Results
Results indicate that in both classes maximum costs are related to excavation section while minimum costs are for invert and mucking. In all concrete spray operations there was just a %3.5 increase in costs. Overall savings in excavation and support was about %10 which is significant (Figure 8).
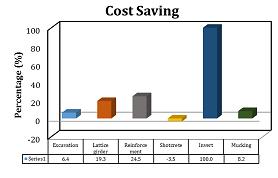 Figure8. Savings percentage comparison in excavation and support classes A and B
Figure8. Savings percentage comparison in excavation and support classes A and B


.jpg)


